Before we delve into the most commonly used Command prompt commands, let’s first make sure our readers know to get there, to begin with.
How to access Windows Command Prompt
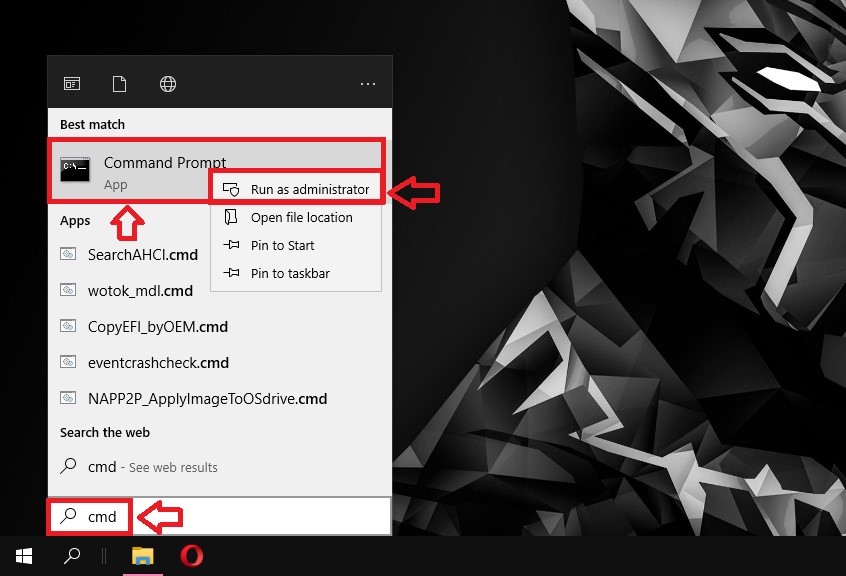
Shortcut: Win + X The quickest way to access Windows Command Prompt is to press the Windows button + X at the same time. This will open a menu with Windows shortcuts, configuration and other management tools. These days though, Windows is pushing PowerShell over Command Prompt so you might find the shortcut switched. Not to worry. Another way to access Windows Command Prompt is to Search for it. In the Search box, type Command Prompt or CMD. If you want to open CMD as an Administrator, right-click on your search result and select Run as Administrator.
Most commonly used Windows Command Prompt Commands
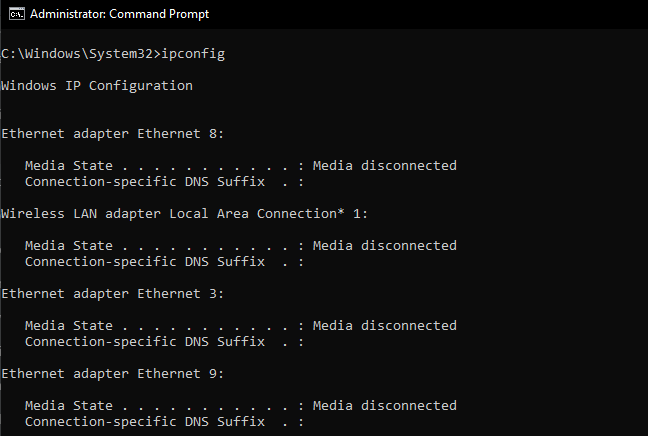
1. Ipconfig
The ipconfig command displays the IP address, subnet mask and default gateway for each adapter bound to TCP/IP (the standard for transmitting data over networks). The ipconfig command can also be modified for other functions. Examples: > ipconfig /all Display full configuration information. > ipconfig / release Release the IPv4 address for the specified adapter. > ipconfig / renew Renew the IPv4 address for the specified adapter. > ipconfig / flushdns Purges the DNS Resolver cache. > ipconfig / registerdns Refreshes all DHCP leases and re-registers DNS names > ipconfig / displaydns Display the contents of the DNS Resolver Cache.
2. Ping
The ping command is used to verify IP-level connectivity between a source computer and a remote computer. The ping command is a simple way to verify that your computer can connect to a network such as other computers or the internet. Often, ping is used to check whether you have an internet connection. Example: > ping dignited.com
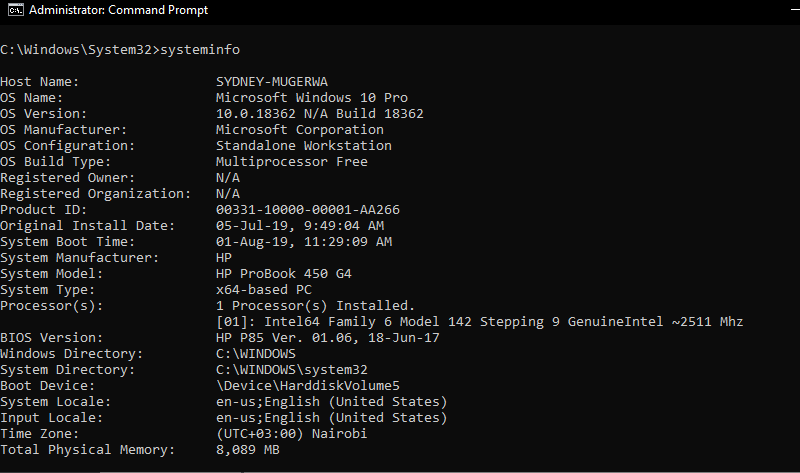
3. Systeminfo
This tool displays operating system configuration information for a local or remote machine, including service pack levels. Systeminfo covers operating system and some hardware information. i.e. Hostname, OS version and Architecture, Bios version, Windows installation date, last boot time, PC model, installed and available RAM, Network card configurations, e.t.cRelated content: Related content:
10 most common Windows Run CommandsHow to rename multiple file extensions in Windows using Command Prompt
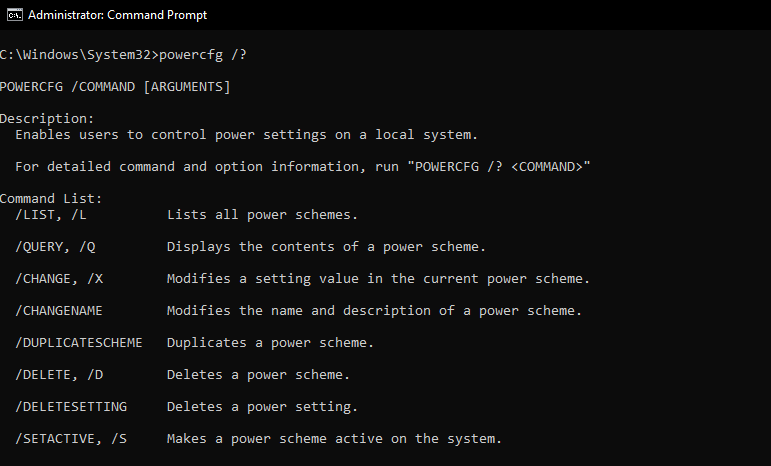
4. Powercfg
The powercfg command allows command-line access to power management tools which are used to manage and track how Windows uses energy. Some of these tools include displaying and listing current power schemes, enabling/disabling hibernate and also analyzing battery life problems to scratch the surface. Heres a list Examples: > powercfg /list (or l) Lists all power schemes. > powercfg /query (or q) Displays the contents of a power scheme. > powercfg /change (or x) Modifies a setting value in the current power scheme. > powercfg /hibernate (or h) Enables and disables the hibernate feature. > powercfg /lastwake Reports information about what woke the system from the last sleep transition. > powercfg /energy Analyzes the system for common energy-efficiency and Battery life problems. > powercfg /batteryreport Generates a report of battery usage. > powercfg /systempowerreport generates a diagnostic system power transition report.
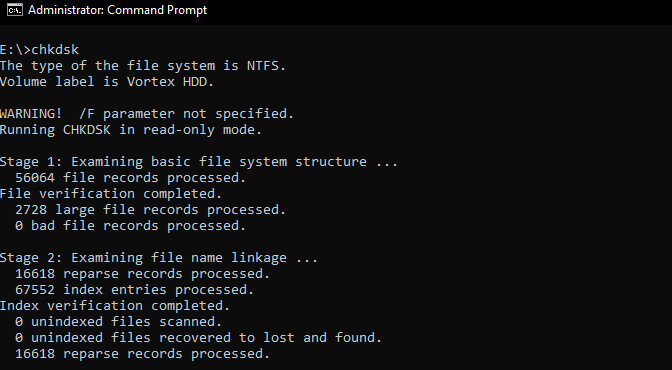
5. Chkdsk (Check Disk)
Check Disk (usually shortened to chkdsk) is used to (you guessed it) check a disk, identify errors or bad sectors and fix those errors. Examples:> chkdsk /f Fixes errors on the disk.> chkdsk /v On FAT/FAT32: Displays the full path and name of every file on the disk. On NTFS: Displays cleanup messages if any.> chkdsk /r Locates bad sectors and recovers readable information (implies /f, when /scan not specified).> chkdsk /scan NTFS only: Runs an online scan on the volume> chkdsk /spotfix NTFS only: Runs spot-fixing on the volume> chkdsk /offlinescanandfix Runs an offline scan and fix on the volume.> chkdsk /freeorphanedchains FAT/FAT32/exFAT only: Frees any orphaned cluster chains instead of recovering their contents.
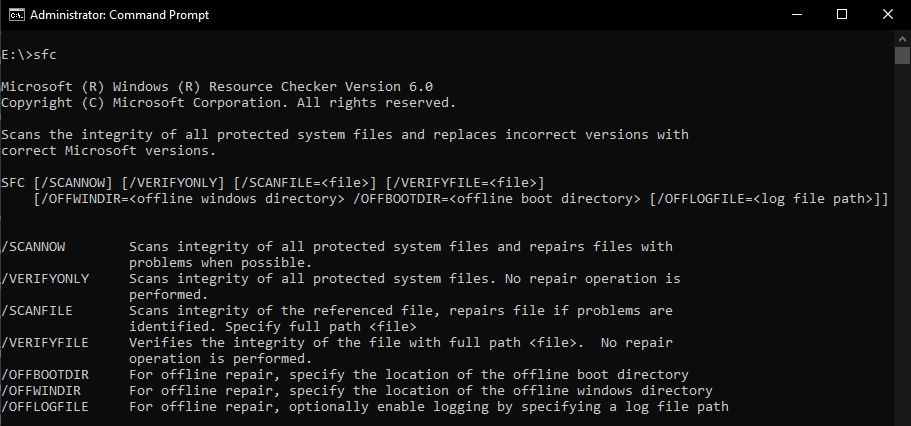
6. Sfc (System File Checker)
Sfc (an abbreviation for System File Checker) is a vital command prompt command which verifies the integrity of Windows system files. Subsequently, is also used to replace incorrect files with the correct Microsoft versions. Examples:> sfc /scannow Scans integrity of all protected system files and repairs files with problems when possible.> sfc /verifyonly Scans integrity of all protected system files. No repair operation is performed.> sfc /scanfile Scans integrity of the referenced file, repairs file if problems are identified. Specify full path > sfc /verifyfile Verifies the integrity of the file with full path. No repair operation is performed.
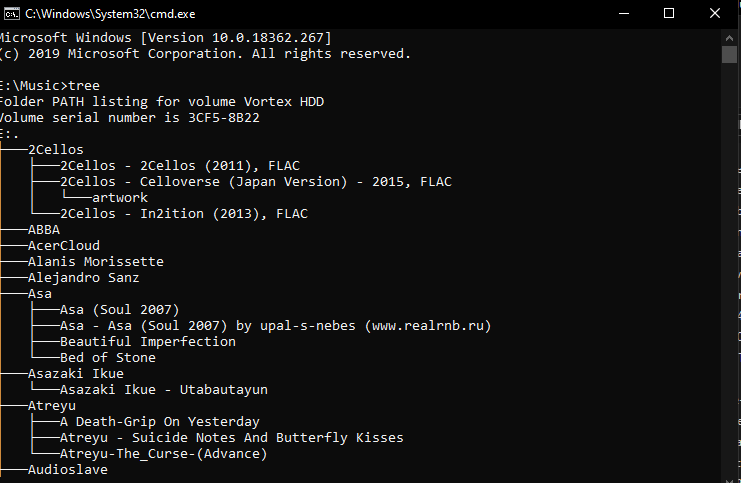
7. Tree
The Tree command graphically displays the folder structure of a drive or path. In layman’s terms, Tree shows you the content of a drive or a path. You can use it to copy a list of the files you have in a directory (e.g. music or movies.)
8. Attrib (Attribute)
The attrib command displays or changes file attributes of a single file or of a directory. The most common usage of this command is to unhide files on flash drives. Tip: How to unhide files on a flash drive using attrib:> attrib -h -r -s /s /d G:. (replace G: with current device drive letter)